Generate Ssh Key Pair Windows 10
- Generate Ssh Key On Windows 10
- Generate Ssh Key Pair Windows 10 With Printer
- Create Ssh Key Pair Windows 10
Oct 24, 2016 Can Windows 10 Generate SSH Key-Pairs for SSH Access to Itself? Window 10 Pro. There are registry tweaks needed to tell windows 'Hey, use this key-pair for david.' , I need that information as well. I've searched the Microsoft site to no avail. It is like ssh'ing into your OS is an undocumented concept. Sep 26, 2019 First, create the SSH directory and then generate the SSH key pair. One assumption is that the Windows profile you are using is set up with administrative privileges. Given this, you will be creating the SSH directory at the root of your profile, for example: C: Users joetest. At the Git Bash command line, change into your root directory and type.
- Jul 29, 2019 The ssh-keygen command creates a 2048-bit RSA key pair. For extra security, use RSA4096: ssh –keygen –t rsa 4096. If you’ve already generated a key pair, this will prompt to overwrite them, and those old keys will not work anymore. The system will ask you to create a passphrase as an added layer of security.
- Key generation with PuTTY. To generate a key pair with the PuTTY key generator, simply run puttygen.exe and click the Generate button in the window that appears. You will be asked to move the mouse and press keys to improve the random number generation at the heart of SSH security.
- Jul 29, 2019 The ssh-keygen command creates a 2048-bit RSA key pair. For extra security, use RSA4096: ssh –keygen –t rsa 4096. If you’ve already generated a key pair, this will prompt to overwrite them, and those old keys will not work anymore. The system will ask you to create a passphrase as an added layer of security.
This article describes ways to generate and use secure shell (SSH) keys on a Windows computer to create and connect to a Linux virtual machine (VM) in Azure. To use SSH keys from a Linux or macOS client, see the quick or detailed guidance.
Overview of SSH and keys
SSH is an encrypted connection protocol that allows secure sign-ins over unsecured connections. SSH is the default connection protocol for Linux VMs hosted in Azure. Although SSH itself provides an encrypted connection, using passwords with SSH connections still leaves the VM vulnerable to brute-force attacks or guessing of passwords. A more secure and preferred method of connecting to a VM using SSH is by using a public-private key pair, also known as SSH keys.
The public key is placed on your Linux VM, or any other service that you wish to use with public-key cryptography.
The private key remains on your local system. Protect this private key. Do not share it.
When you use an SSH client to connect to your Linux VM (which has the public key), the remote VM tests the client to make sure it possesses the private key. If the client has the private key, it's granted access to the VM.
Depending on your organization's security policies, you can reuse a single public-private key pair to access multiple Azure VMs and services. You do not need a separate pair of keys for each VM or service you wish to access.
Your public key can be shared with anyone, but only you (or your local security infrastructure) should possess your private key.
Supported SSH key formats

Azure currently supports SSH protocol 2 (SSH-2) RSA public-private key pairs with a minimum length of 2048 bits. Other key formats such as ED25519 and ECDSA are not supported.
Windows packages and SSH clients
You connect to and manage Linux VMs in Azure using an SSH client. Computers running Linux or macOS usually have a suite of SSH commands to generate and manage SSH keys and to make SSH connections.
Windows computers do not always have comparable SSH commands installed. Recent versions of Windows 10 provide OpenSSH client commands to create and manage SSH keys and make SSH connections from a command prompt. Recent Windows 10 versions also include the Windows Subsystem for Linux to run and access utilities such as an SSH client natively within a Bash shell.
Other common Windows SSH clients you can install locally are included in the following packages:
Generate Ssh Key On Windows 10
You can also use the SSH utilities available in Bash in the Azure Cloud Shell.
- Access Cloud Shell in your web browser at https://shell.azure.com or in the Azure portal.
- Access Cloud Shell as a terminal from within Visual Studio Code by installing the Azure Account extension.
Create an SSH key pair
The following sections describe two options to create an SSH key pair on Windows. You can use a shell command (ssh-keygen) or a GUI tool (PuTTYgen). Also note, when using Powershell to create a key, upload the public key as ssh.com(SECSH) format. When using CLI, convert the key into OpenSSH format prior to uploading.
Create SSH keys with ssh-keygen
If you run a command shell on Windows that supports SSH client tools (or you use Azure Cloud Shell), create an SSH key pair using the ssh-keygen command. Type the following command, and answer the prompts. If an SSH key pair exists in the chosen location, those files are overwritten.
Generate Ssh Key Pair Windows 10 With Printer
For more background and information, see the quick or detailed steps to create SSH keys using ssh-keygen.
Create SSH keys with PuTTYgen
If you prefer to use a GUI-based tool to create SSH keys, you can use the PuTTYgen key generator, included with the PuTTY download package.
To create an SSH RSA key pair with PuTTYgen:
Start PuTTYgen. Vb.net product key generator.
Click Generate. By default PuTTYgen generates a 2048-bit SSH-2 RSA key.
Move the mouse around in the blank area to provide randomness for the key.
After the public key is generated, optionally enter and confirm a passphrase. You will be prompted for the passphrase when you authenticate to the VM with your private SSH key. Without a passphrase, if someone obtains your private key, they can sign in to any VM or service that uses that key. We recommend you create a passphrase. However, if you forget the passphrase, there is no way to recover it.
The public key is displayed at the top of the window. You can copy this entire public key and then paste it into the Azure portal or an Azure Resource Manager template when you create a Linux VM. You can also select Save public key to save a copy to your computer:
Optionally, to save the private key in PuTTy private key format (.ppk file), select Save private key. You will need the .ppk file later to use PuTTY to make an SSH connection to the VM.
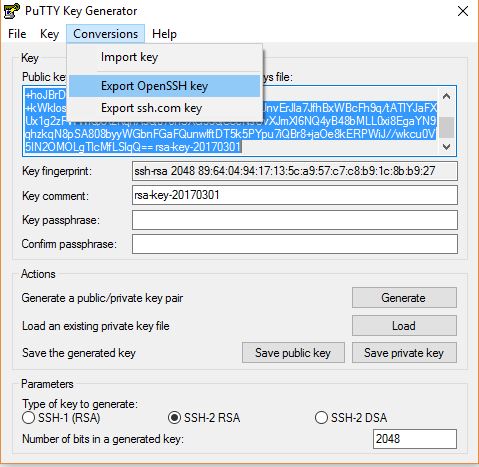
If you want to save the private key in the OpenSSH format, the private key format used by many SSH clients, select Conversions > Export OpenSSH key.
Provide an SSH public key when deploying a VM
To create a Linux VM that uses SSH keys for authentication, provide your SSH public key when creating the VM using the Azure portal or other methods.
The following example shows how you would copy and paste this public key into the Azure portal when you create a Linux VM. The public key is typically then stored in the ~/.ssh/authorized_key directory on your new VM.
Connect to your VM
One way to make an SSH connection to your Linux VM from Windows is to use an SSH client. This is the preferred method if you have an SSH client installed on your Windows system, or if you use the SSH tools in Bash in Azure Cloud Shell. If you prefer a GUI-based tool, you can connect with PuTTY.
Use an SSH client
With the public key deployed on your Azure VM, and the private key on your local system, SSH to your VM using the IP address or DNS name of your VM. Replace azureuser and myvm.westus.cloudapp.azure.com in the following command with the administrator user name and the fully qualified domain name (or IP address):
If you configured a passphrase when you created your key pair, enter the passphrase when prompted during the sign-in process.
If the VM is using the just-in-time access policy, you need to request access before you can connect to the VM. For more information about the just-in-time policy, see Manage virtual machine access using the just in time policy.
Connect with PuTTY
If you installed the PuTTY download package and previously generated a PuTTY private key (.ppk) file, you can connect to a Linux VM with PuTTY.
Start PuTTy.
Fill in the host name or IP address of your VM from the Azure portal:
Select the Connection > SSH > Auth category. Browse to and select your PuTTY private key (.ppk file):
Click Open to connect to your VM.
Next steps
For detailed steps, options, and advanced examples of working with SSH keys, see Detailed steps to create SSH key pairs.
You can also use PowerShell in Azure Cloud Shell to generate SSH keys and make SSH connections to Linux VMs. See the PowerShell quickstart.
If you have difficulty using SSH to connect to your Linux VMs, see Troubleshoot SSH connections to an Azure Linux VM.
The PuTTYgen program is part of PuTTY, an open source networking client for the Windows platform.
Create Ssh Key Pair Windows 10
- Download and install PuTTY or PuTTYgen.
To download PuTTY or PuTTYgen, go to http://www.putty.org/ and click the You can download PuTTY here link.
- Run the PuTTYgen program.
- Set the Type of key to generate option to SSH-2 RSA.
- In the Number of bits in a generated key box, enter 2048.
- Click Generate to generate a public/private key pair.
As the key is being generated, move the mouse around the blank area as directed.
- (Optional) Enter a passphrase for the private key in the Key passphrase box and reenter it in the Confirm passphrase box.
Note:
While a passphrase is not required, you should specify one as a security measure to protect the private key from unauthorized use. When you specify a passphrase, a user must enter the passphrase every time the private key is used.
This allows anyone downloading or receiving the file to verify (to some extent) that the file has not been tampered with. Normally the canonical author of a file will also publish the SHA-1 of the file. Generate sha1 key. It is worth verifying that the published SHA-1 also matches the one published by the author on any webpage relating to the download. Sha1sum somefile.txt somefile.txt.sha1cat somefile.txt.sha1da39a3ee5e6b4b0d3255bfef95601890afd80709 somefile.txtIf the file somefile.txt is to be distributed on the Internet the accompanying SHA-1 file can be distributed with it.
- Click Save private key to save the private key to a file. To adhere to file-naming conventions, you should give the private key file an extension of
.ppk(PuTTY private key).Note:
The.ppkfile extension indicates that the private key is in PuTTY's proprietary format. You must use a key of this format when using PuTTY as your SSH client. It cannot be used with other SSH client tools. Refer to the PuTTY documentation to convert a private key in this format to a different format. - Select all of the characters in the Public key for pasting into OpenSSH authorized_keys file box.
Make sure you select all the characters, not just the ones you can see in the narrow window. If a scroll bar is next to the characters, you aren't seeing all the characters.
- Right-click somewhere in the selected text and select Copy from the menu.
- Open a text editor and paste the characters, just as you copied them. Start at the first character in the text editor, and do not insert any line breaks.
- Save the text file in the same folder where you saved the private key, using the
.pubextension to indicate that the file contains a public key. - If you or others are going to use an SSH client that requires the OpenSSH format for private keys (such as the
sshutility on Linux), export the private key:- On the Conversions menu, choose Export OpenSSH key.
- Save the private key in OpenSSH format in the same folder where you saved the private key in
.ppkformat, using an extension such as.opensshto indicate the file's content.